Automated EEG Electrode Localization with Flying Triangulation
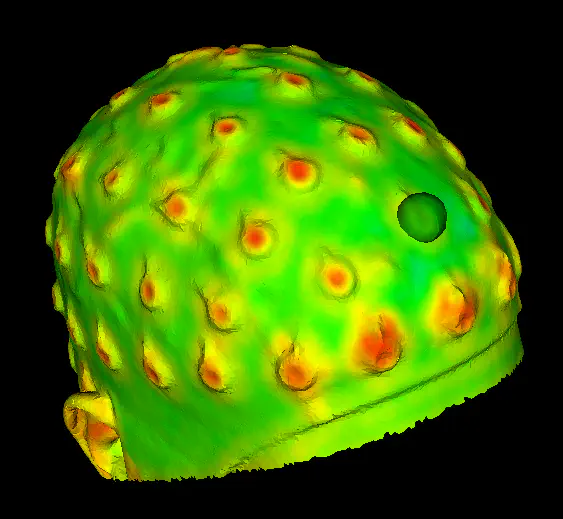
This project demonstrates an automated, contactless method for precisely localizing the 3D positions of electrodes on an electroencephalography (EEG) recording cap. Traditional methods require manually touching each electrode with an electromagnetic digitizer, which can introduce positioning errors.
Our novel approach uses the “Flying Triangulation” optical 3D sensor to scan the subject’s head while wearing the EEG cap. A dense 3D model is generated from the scan data. Sophisticated algorithms then automatically detect the center point of each electrode in the 3D model, using one electrode as a reference template.
Validation showed the Flying Triangulation approach determined electrode positions with 1.5 mm average deviation, a significant improvement over the 6.8 mm deviation of the standard contact-based method. This enables more accurate neurosurgical planning based on precise, user-independent localization of EEG electrodes.
The key advantages are: Completely contactless and automated Reduces positioning errors compared to manual methods Simple and fast 3D acquisition using a compact handheld sensor Motion-robust scanning of complex shapes like the human head